Routing Public IP Addresses¶
This section covers the routing of public IP addresses where a public IP subnet is assigned to an internal interface on a single firewall deployment.
See also
If a High Availability cluster is in use, see High Availability Configuration Example without NAT.
IP Assignments¶
At least two public IP subnets must be assigned by the ISP. One is for the WAN of the firewall, and one for the inside interface. This is commonly a /30 subnet for the WAN, with a second subnet assigned for the internal interface. This example will use a /30 on WAN as shown in Table WAN IP Block and a /29 public subnet on an internal OPT interface as shown in Table Inside IP Block.
198.51.100.64/30 |
|
|---|---|
IP Address |
Assigned To |
198.51.100.65 |
ISP router (pfSense® default gateway) |
198.51.100.66 |
pfSense WAN interface IP address |
192.0.2.128/29 |
|
|---|---|
IP Address |
Assigned To |
192.0.2.129 |
pfSense OPT interface |
192.0.2.130 |
Internal hosts |
192.0.2.131 |
|
192.0.2.132 |
|
192.0.2.133 |
|
192.0.2.134 |
|
Interface Configuration¶
First configure the WAN and OPT interfaces. The LAN interface can also be used for public IP addresses if desired. In this example, LAN is a private IP subnet and OPT1 is the public IP subnet.
Configure WAN¶
Add the IP address and gateway accordingly. Figure WAN IP and Gateway Configuration shows the WAN configured as shown in Table WAN IP Block.
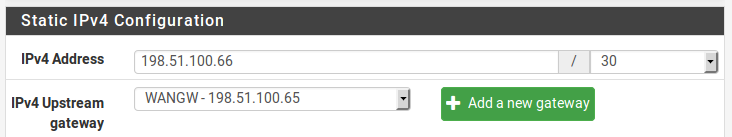
WAN IP and Gateway Configuration¶
Configure OPT1¶
Now enable OPT1, optionally change its name, and configure the IP address and subnet mask. Figure Routing OPT1 Interface Configuration shows OPT1 configured as shown in Table Inside IP Block.
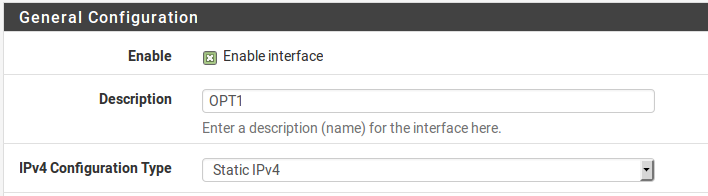
Routing OPT1 Interface Configuration¶
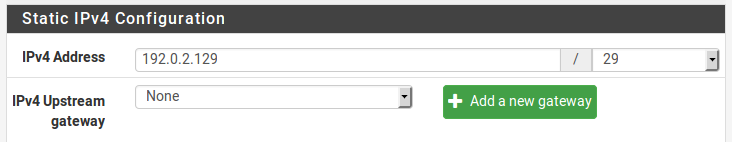
Routing OPT1 IP Address Configuration¶
NAT Configuration¶
The default of translating internal traffic to the WAN IP must be overridden when using public IP addresses on an internal interface.
Browse to Firewall > NAT
Click the Outbound tab
Select Hybrid Outbound NAT rule generation
Click Save
Click
 to add a new rule to the top of the list with the following
settings:
to add a new rule to the top of the list with the following
settings:- Do not NAT:
Checked, so that NAT will be disabled
- Interface:
WAN
- Protocol:
Any
- Source:
Network, enter the local public IP subnet,
192.0.2.128/29- Destination:
Any
Click Save
This will override the default automatic rules which translate all traffic from
local interfaces leaving the WAN interface to the WAN IP address. Traffic
sourced from the OPT1 network 192.0.2.128/29 is not translated because of
the manually added rule excluding it from NAT. This configuration maintains the
automatic behavior for other internal interfaces, so that the advantages of
automatic outbound NAT rules are not lost. This configuration is shown in Figure
Outbound NAT Configuration.
If public IP addresses are used on all local interfaces, then set Disable Outbound NAT rather than using Hybrid mode.
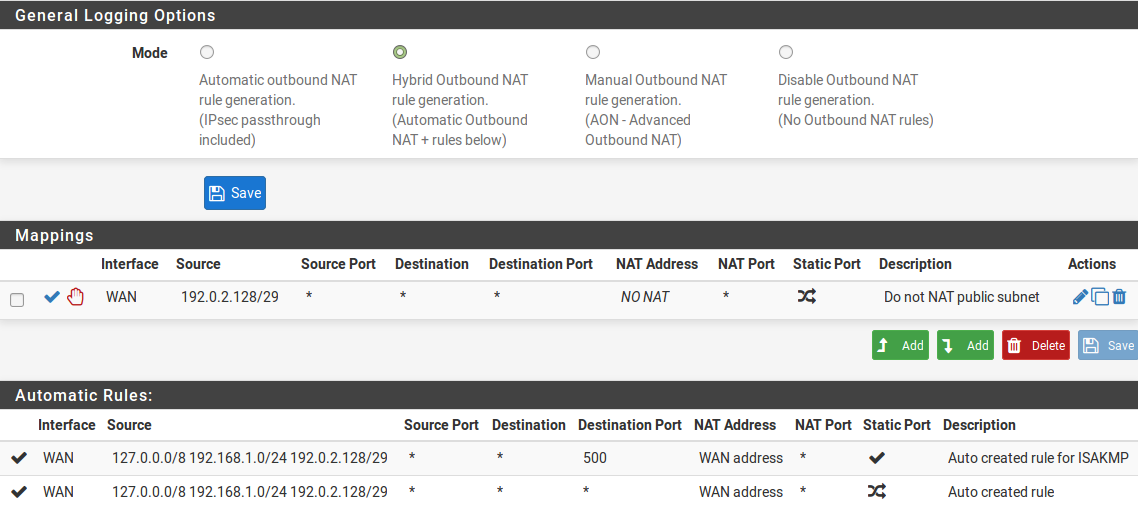
Outbound NAT Configuration¶
Firewall Rule Configuration¶
The NAT and IP address configuration is now complete. Firewall rules will need to be added to permit outbound and inbound traffic. Figure OPT1 Firewall Rules shows a DMZ-like configuration, where all traffic destined for the LAN subnet is rejected, DNS and pings to the OPT1 interface IP address are permitted, and HTTP is allowed outbound.
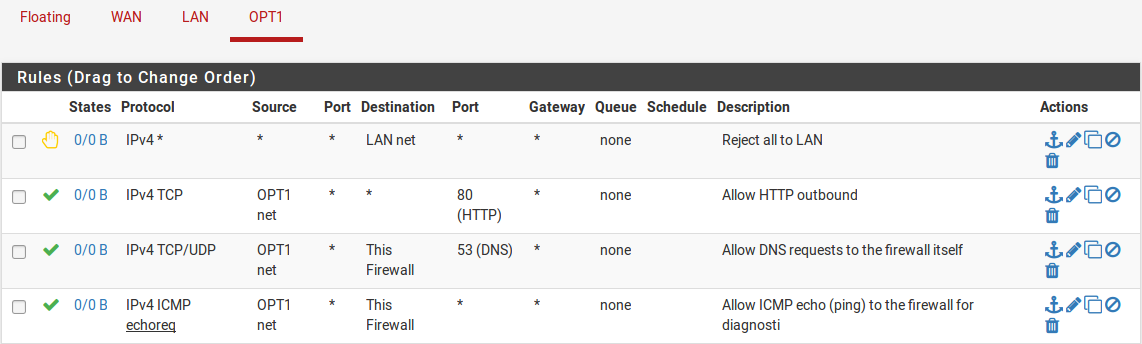
OPT1 Firewall Rules¶
To allow traffic from the Internet to the public IP addresses on an internal interface, add rules on the WAN using the public IP addresses as the Destination. Figure WAN Firewall Rules shows a rule that allows HTTP to 192.0.2.130, one of the public IP addresses on the internal interface as shown in Table Inside IP Block.

WAN Firewall Rules¶
After configuring the firewall rules as desired, the setup is complete.
Note
Traffic will flow from LAN to this public subnet by default without NAT. If this behavior is not desired, adjust the LAN firewall and NAT rules accordingly. Additionally, policy routing may need to be bypassed to allow from LAN to this interface.