High Availability Configuration Example with Multi-WAN¶
High availability (HA) can be deployed for firewall redundancy in a multi-WAN configuration. This section details the VIP and NAT configuration needed for a dual WAN HA deployment.
Note
This recipe is a supplement to High Availability Configuration Example. Read through that recipe before proceeding. This document only covers topics specific to high availability and multi-WAN and is not a complete HA configuration guide.
See also
Determine IP Address Assignments¶
This example uses four IPv4 addresses on each WAN. Each firewall needs an IP address, plus one CARP VIP for Outbound NAT, plus an additional CARP VIP for a 1:1 NAT entry that will be used for an internal mail server in the DMZ segment.
WAN and WAN2 IP Addresses¶
Table WAN IP Addresses shows the IP addresses for both WANs. In most environments these will be public IP addresses.
IP Address |
Usage |
|---|---|
|
Shared CARP VIP for Outbound NAT |
|
Primary firewall WAN |
|
Secondary firewall WAN |
|
Shared CARP VIP for 1:1 NAT |
IP Address |
Usage |
|---|---|
|
Shared CARP VIP for Outbound NAT |
|
Primary firewall WAN2 |
|
Secondary firewall WAN2 |
|
Shared CARP VIP for 1:1 NAT |
LAN Addresses¶
The LAN subnet is 192.168.1.0/24. For this example, the LAN IP addresses are
assigned as described in Table LAN IP Address Assignments:
IP Address |
Usage |
|---|---|
|
CARP shared LAN VIP |
|
Primary firewall LAN |
|
Secondary firewall LAN |
DMZ Addresses¶
The DMZ subnet is 192.168.2.0/24. For this example, the DMZ IP addresses are
assigned as described in Table DMZ IP Address Assignments:
IP Address |
Usage |
|---|---|
|
CARP shared DMZ VIP |
|
Primary firewall DMZ |
|
Secondary firewall DMZ |
Sync Interface Addressing¶
There will be no shared CARP VIP on the Sync interface because there is no need
for one. These IP addresses are used only for communication between the HA
nodes. For this example, 172.16.1.0/24 is the Sync subnet. The two nodes
only require one IP address each (two total), but the example uses a /24
size subnet to be consistent with the other internal interfaces. For the last
octet of the IP addresses, use the same last octet as the LAN IP address on that
node for consistency.
IP Address |
Usage |
|---|---|
|
Primary firewall Sync |
|
Secondary firewall Sync |
NAT Configuration¶
The NAT configuration when using HA with Multi-WAN is the same as HA with a single WAN, except the rules are repeated, so there is a set for each WAN. Ensure that only CARP VIPs are used for inbound traffic or routing.
See also
See Network Address Translation for more information on NAT configuration.
Firewall Configuration¶
With Multi-WAN a firewall rule must be in place to pass traffic to local networks using the default gateway. Otherwise, when traffic attempts to reach the CARP address or from LAN to DMZ it will instead go out a WAN connection.
Add a rule at the top of the firewall rules for all internal interfaces which will direct traffic for all local networks to the default gateway. The important part is the gateway must be default for this rule and not one of the failover or load balance gateway groups. The destination for this rule would be the local LAN network, or an alias containing any locally reachable networks.
See also
Multi-WAN HA with DMZ Diagram¶
Due to the additional WAN and DMZ elements, a diagram of this layout is much more complex as can be seen in Figure Diagram of Multi-WAN HA with DMZ.
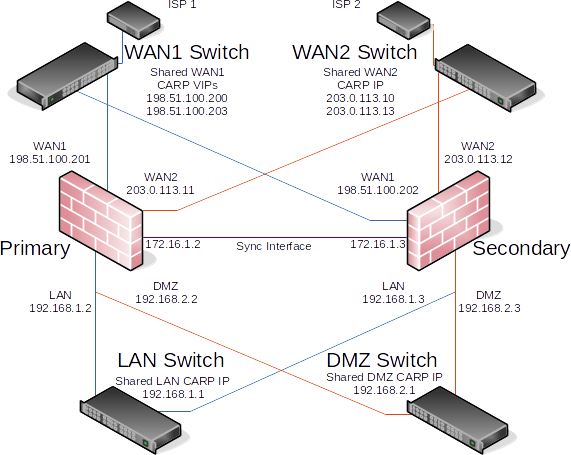
Diagram of Multi-WAN HA with DMZ¶