High Availability Configuration Example without NAT¶
High Availability (HA) can provide redundancy for routed public subnets. This section describes this type of configuration, which is common in large networks, ISP, wireless ISP networks, and data center environments.
Note
This recipe is a supplement to High Availability Configuration Example. Read through that recipe before proceeding. This document only covers topics specific to high availability without NAT and is not a complete configuration guide.
As mentioned in High Availability Configuration Example, CARP VIPs are the only type of VIPs which provide redundancy for addresses directly handled by the firewall, and CARP VIPs can only be used in conjunction with NAT or services on the firewall itself. However, sources can send traffic to the CARP VIPs, such as delivering traffic from routed subnets, and it will reach the active node for processing even if it isn’t involved in NAT or local services.
Note
This recipe only covers IPv4 without NAT as the IPv6 configuration in High Availability Configuration Example does not involve NAT, so there are no differences to address.
Public IPv4 Address Assignments¶
HA requires at least a /29 block of public IPv4 addresses for the WAN side
of the firewall, which provides six usable IPv4 addresses. Each firewall
requires one IPv4 address, and at least one CARP VIP on the WAN side. A two node
deployment only requires three addresses, but this is the smallest subnet that
will accommodate three usable IPv4 addresses since the upstream router consumes
one, and two are lost to the network and broadcast addresses.
Additional public IPv4 address subnets for internal use must be routed to one of
the WAN CARP VIPs by the ISP, data center, or upstream router. When the upstream
source routes additional subnets to a CARP VIP, the routing will not be
dependent upon a single node. The example configuration depicted in this section
uses a /24 public IPv4 subnet and splits it into two /25 subnets.
Network Overview¶
The example network depicted here is a data center environment consisting of two HA nodes with four interfaces each: WAN, WEB (LAN), DBDMZ, and Sync. This network contains a number of web and database servers. It is not based on any real network, but there are countless similar production deployments.
WAN¶
The WAN side connects to the upstream network, which may be an ISP, a data center, upstream router, or other means of external connectivity.
WEB Network¶
The WEB segment in this network uses the “LAN” interface but renamed. It contains web servers, so it has been named WEB, but it could be called DMZ, SERVERS, or anything desired.
DBDMZ Network¶
This segment is an OPT interface and contains database servers. It is common to segregate web and database servers into separate networks in hosting environments. The database servers typically do not require direct access from the Internet, and hence are better protected against remote compromise than web servers.
Sync Network¶
The HA nodes use the Sync network in this diagram to replicate configuration changes via XMLRPC and for state synchronization to replicate state table changes between the two firewalls. As described in other HA documentation sections, the best practice is to use a dedicated interface for this purpose.
Network Layout¶
Figure Diagram of HA with Routed IPv4 Subnets illustrates this network layout, including all routable IP addresses, the WEB network, and the Database DMZ.
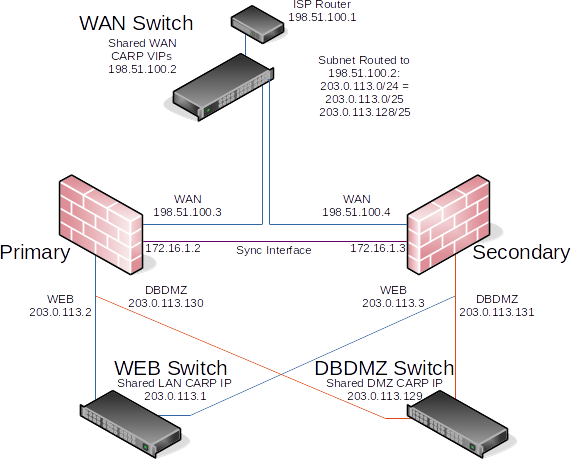
Diagram of HA with Routed IPv4 Subnets¶
Note
Segments containing database servers typically do not need to be publicly accessible, and hence would more commonly use private IP subnets, but the example illustrated here can be used regardless of the function of the two internal subnets.
Outbound NAT¶
The Outbound NAT Mode in Firewall > NAT on the Outbound NAT tab must be set to Manual to properly accommodate this scenario. When the mode is set to Manual, saving the settings creates a set of outbound NAT rules equivalent to the rules which were utilized in Automatic or Hybrid modes.
In the list of rules created by switching to Manual Outbound NAT, delete any rules which translate sources using the routed subnets (e.g. WEB Networks, DBDMZ Networks). This effectively disables NAT for the routed subnets.
Warning
Do not delete outbound NAT rules that translate from a source of
Localhost (127.0.0.1) using the WAN interface address(es) as these are
necessary to ensure traffic from the firewall itself can egress properly.
See also
Firewall Rules¶
Firewall rules in this scenario are much simpler as there is no need to consider NAT translation. Allow traffic directly to the necessary destinations as needed.
Warning
As there is no NAT involved, carefully crafting WAN rules becomes more critical as being overly permissive with WAN rules not only can allow remote attackers access to the firewall itself, but all local networks.
Ensure the rules properly segment the DBDMZ from the WEB network; Block or reject any traffic between the segments except what is absolutely required for necessary functionality. For example, only allow connections from web servers to the database port(s) and nothing else.
Note
Best practices and requirements vary wildly in this regard depending on the operating systems and other software involved. Consult documentation for the servers to determine requirements.
See also