NTP Daemon Status¶
The NTP status page at Status > NTP shows the status of the NTP daemon. This status includes information on upstream NTP servers as well as other items such as GPS information if such a device is connected and enabled.
An example of the status is shown in Figure NTP Daemon Status With GPS Output.
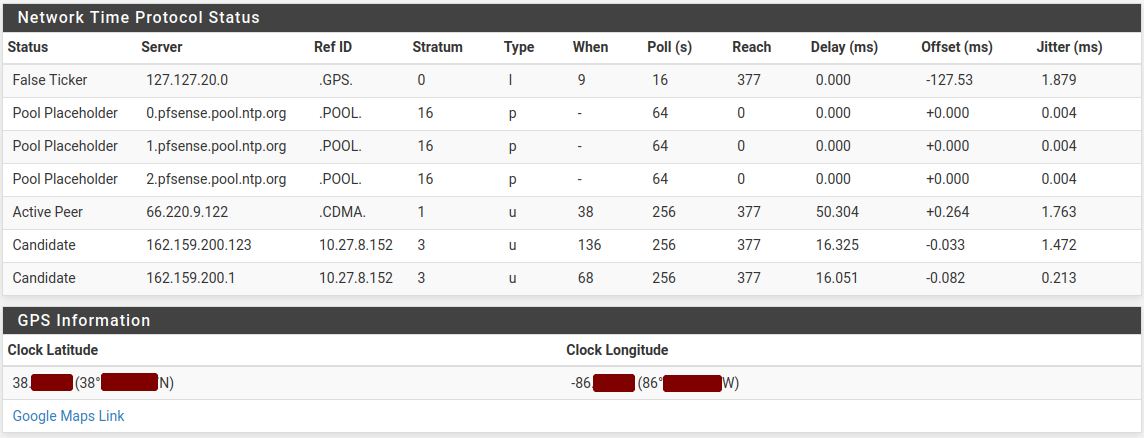
NTP Daemon Status With GPS Output¶
The status screen contains one line for every peer, and each entry contains the following items:
- Status:
The current status of the NTP server entry, which may be one of:
- Pool Placeholder:
Placeholder entry for pools defined in the configuration. When using a pool, these are the entries in the NTP configuration and the NTP daemon dynamically discovers the servers based on the DNS response for the pool address.
- Unreach/Pending:
The server is either unreachable or it has not yet responded with sufficient information to determine a better status.
- Active Peer:
The NTP server with which the daemon is currently synchronizing its clock.
- Candidate:
A peer which has a high enough quality status to become an active peer.
- PPS Peer:
A peer utilizing PPS signaling.
- Selected:
A peer which is included by the combine algorithm.
- Excess Peer:
An excess peer which is not included because there are too many other viable peers.
- False Ticker:
A peer which has been rejected by the intersection algorithm.
- Outlier:
A peer which has been discarded by the cluster algorithm.
See also
For more information on the algorithms involved in determining status, see the NTP documentation page on Clock Select Algorithm.
- Server:
The hostname or IP address of the NTP server. For pool placeholders, this is the FQDN of the pool.
Some special sources such as a local NMEA reference clock like a GPS use reserved addresses. A GPS, for example, appear as an address in
127.127.20.x.- Ref ID:
A reference ID indicating how this NTP server is determining its own time.
This is typically a source IP Address for higher stratum servers (
2or higher) which is used by clients to prevent a loop where servers might reference each other which could lead to inaccuracies.Stratum 1 servers are considered reference clocks. For these servers this reference ID is a four character string indicating the type of reference used to determine the NTP server’s own time. There are a handful of pre-defined codes in RFC 5905, but servers can use custom codes as well.
Some commonly observed reference ID codes are:
- POOL:
This is a pool placeholder entry and not a source.
- GPS:
This NTP server determines its time based on a GPS device.
- PPS:
This NTP server determines its time based on a PPS device.
- CDMA:
This NTP server determines its time based on a CDMA network reference.
Stratum 0 servers are invalid as a time source but offer a four character “Kiss code” indicating a reason why they are not a valid time source at that moment.
See also
For a full list of pre-defined Kiss and Reference ID codes, see the IANA NTP parameter lists.
- Stratum:
The stratum of this NTP server, in the following ranges:
- Stratum 0:
Invalid or unavailable time source.
- Stratum 1:
Reference clocks which use a non-NTP time source to keep time, such as a GPS, atomic clock, etc.
These servers are highly accurate but should not be used directly by clients. They should be used primarily by servers which will offer NTP service to many of their own local clients.
- Stratum 2-14:
NTP servers which obtain their own time from other NTP servers on a lower stratum.
These are typically the best sources for clients to use. Though they are potentially not as accurate as stratum 1 servers, in nearly all cases they are accurate enough for the majority of purposes.
- Stratum 15:
The server is not suitable for synchronizing clients (See the NTP documentation page on Clock Select Algorithm).
- Stratum 16:
Unsynchronized source.
- Type:
A code indicating the type of NTP server:
- u:
Unicast or manycast client
- b:
Broadcast or multicast client
- p:
Pool source
- l:
Local (reference clock)
- s:
Symmetric (peer)
- A:
Manycast server
- B:
Broadcast server
- M:
Multicast server
- When:
The amount of time since the NTP daemon last received a packet from this server. The value is
-if NTP has not received any packets.- Poll(s):
The interval between polls to this server.
- Reach:
Reach shift register, displayed in octal.
- Delay (ms):
Round trip delay to this NTP server.
- Offset (ms):
Clock offset of this NTP server relative to this firewall.
- Jitter (ms):
Offset RMS error estimate.
If a serial GPS is connected and configured, the page also prints the coordinates reported by the GPS device along with a link to the coordinates on Google Maps.
Note
The quality of GPS data can vary widely depending on the signal level, the GPS device, and how it is connected. Traditional serial ports are higher quality and better suited to GPS clock usage. USB serial GPS units may be acceptable, but due to how USB functions, the timing of signals cannot be guaranteed the way it can be with a traditional hard-wired serial port.