DHCPv4 Status¶
The current contents of the DHCPv4 lease database and related information are viewable at Status > DHCP leases.
The page contains multiple sections with information about leases. The exact information and layout depends on the selected DHCP backend.
Pool Status (HA/Failover) – ISC DHCP Only¶
The Pool Status section of the page is only present if the firewall is using the ISC DHCP backend and is configured for DHCPv4 failover as a part of a high availability cluster.
This section of the page includes information on DHCP failover pools, including:
- Failover Group:
The name of the failover group for a given pool, which includes the interface name.
- My State:
The state of the failover pool from the perspective of this firewall.
- Since:
The last time the local pool state changed.
- Peer State:
The state of the failover pool from the perspective of the peer, if known.
- Since:
The last time the peer pool state changed.
DHCPv4 Leases¶
This section of the page lists client leases and their properties, including:
- Status:
The first column with no header contains two icons indicating the current status of the lease. Hover over the icon for a tooltip explaining the meaning of the icon.
- Lease Type:
An icon indicating the type of DHCP lease assigned to this client, which can be one of:
- Static:
This lease entry is from a static DHCP mapping entry.
- Active:
A current lease from an active client.
- Expired:
A lease which has expired because a client did not renew it before its expiration time.
- Online:
An icon indicating whether the device is currently “online” as determined by the contents of the ARP table.
If a system shows online, then it has recently tried to communicate to or through this firewall.
A host marked as offline may be powered on and working, but it has not attempted communication to or through the firewall recently.
- IP Address:
IP address assigned to the client by DHCP, or static mapping address.
- MAC Address:
The client MAC address.
Tip
Installing the NMAP package activates a feature which allows the page to also display the manufacturer associated with the MAC address, if it is known. Note that this is not effective in some cases, such as for virtual machines which use randomly generated MAC addresses or for wireless clients which utilize privacy features that alter their MAC addresses.
- Hostname:
The hostname (if any) that the client sent as part of its DHCP request.
- Description:
The description for a host with a DHCP static mapping.
- Start/End:
The beginning and end times of the DHCP lease.
Note
For static mappings the page prints
n/aas static mapping leases do not have a start or end time, and they do not expire.- Actions:
Icons to take action on this lease. See Actions for details.
Search¶
The search box filters the contents of the Leases table based on keyword matching.
Enter a search string or UNIX regular expression into the box and click Search to filter the list to only matching records.
By default, the search looks at text from all fields in the lease record, but this can be limited to specific fields using the drop-down list.
Actions¶
Add static mapping¶
To create a static mapping from a dynamic lease, click  the to the right of the lease. This pre-fills the MAC address of that host into
the Edit static mapping screen.
the to the right of the lease. This pre-fills the MAC address of that host into
the Edit static mapping screen.
Edit static mapping¶
Entries for existing static mappings have the  icon which takes the
user to the page to edit that specific entry.
icon which takes the
user to the page to edit that specific entry.
Wake on LAN Integration¶
Clicking the  icon to the right of the lease sends a Wake on LAN
(WOL) packet to that host.
icon to the right of the lease sends a Wake on LAN
(WOL) packet to that host.
Click  to create a WOL entry for the MAC address.
to create a WOL entry for the MAC address.
See also
Delete a lease¶
While viewing the leases, an expired or inactive lease may be manually deleted
by clicking  at the end of its line. This option is not available
for active or static leases, only for offline or expired leases.
at the end of its line. This option is not available
for active or static leases, only for offline or expired leases.
Pool Usage Summary¶
The Lease Utilization section summarizes pool usage, giving a count of leases used in each pool configured in the DHCPv4 server.
View inactive leases¶
By default, the page lists active and static leases. Clicking Show all configured leases makes the page display all leases, including inactive and expired leases.
To reduce the view back to normal, click Show active and static leases only.
Clear All DHCP Leases¶
The  Clear all DHCP leases button stops the DHCP daemon,
removes the entire lease database, and then starts the daemon again.
Clear all DHCP leases button stops the DHCP daemon,
removes the entire lease database, and then starts the daemon again.
This does not remove static DHCP leases, only dynamic leases.
High Availability Status – Kea DHCP Only¶
Failover status for Kea DHCP is in a section at the bottom of the DHCP and DHCPv6 Leases pages as in figure Kea DHCP Failover Status - Primary node, both online. The failover status works identically for both DHCP and DHCPv6.
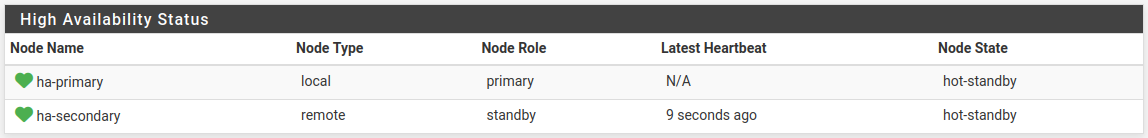
Kea DHCP Failover Status - Primary node, both online¶
The failover section contains a row for each node with the status of each node using the following fields:
- Node Name:
An icon indicating the status of a node followed by the configured name for each node.
The possible icons are:
 : The node is online and has responded recently.
: The node is online and has responded recently. : The node is in an interrupted state, indicating it has not
responded recently and may be going offline.
: The node is in an interrupted state, indicating it has not
responded recently and may be going offline. : The node is in an offline state because it is
unresponsive.
: The node is in an offline state because it is
unresponsive.
- Node Type:
Indicates whether this entry is local (this node) or remote (the peer).
- Node Role:
The selected role for this node (primary or standby).
- Latest Heartbeat:
Elapsed time since this node received a heartbeat from the peer.
- Node State:
The current state of the node, which may be one of the following:
- waiting:
The node is waiting for a connection from the peer.
- syncing:
The node has established a connection with the peer and is synchronizing lease data.
- ready:
The node has finished synchronizing lease data and is ready to serve clients.
- hot-standby:
On a primary node this indicates the node is handing out leases for local clients, coordinating lease data with the secondary node, and sending failover heartbeats.
On a standby node this indicates the node is receiving lease data from the primary node, and sending failover heartbeats, but it is not handing out leases.
- unavailable:
The node is not responding and is considered offline.
- partner-down:
A standby node has assumed an active role in handing out leases for clients since the primary peer is offline.