QinQ Configuration¶
QinQ, also known as IEEE 802.1ad or stacked VLANs, is a means of nesting VLAN tagged traffic inside of packets that are already VLAN tagged, or “double tagging” the traffic.
See also
QinQ is used to move groups of VLANs over a single link containing one outer tag, as can be found on some links between locations from ISPs or datacenters. QinQ can be a quick and easy way of trunking VLANs across locations without having a trunking-capable connection between the sites, provided the infrastructure between the locations does not strip tags from the packets.
QinQ Interface Settings¶
When creating or editing a QinQ interface entry, the following options are available:
- Parent Interface:
The interface that will carry the QinQ traffic.
- VLAN Tag Type:
The VLAN tag protocol identifier (TPID) which specifies the type of VLAN tag in a packet. This can be one of two values:
- C-Tag:
“Customer” tag, value
0x8100. When a packet has multiple tags, C-Tags are the inner tag.- S-Tag:
“Service” tag, value
0x88a8. This is the default and most common value for typical 802.1ad QinQ interfaces. In the majority of cases, S-tags are used for the outer tag when double tagging with QinQ.
- First level tag:
The outer VLAN ID on the QinQ interface, or the VLAN ID given by the provider for the site-to-site link.
- Adds interface to QinQ interface groups:
When checked, a new interface group will be created called QinQ that can be used to filter all the QinQ sub-interfaces at once.
When hundreds or potentially thousands of QinQ tags are present, this greatly reduces the amount of work needed to use the QinQ interfaces
- Description:
Optional text for reference, used to identify the entry
- Member(s):
Member VLAN IDs for QinQ tagging. These can be entered one per row or in ranges such as
100-150.Click
 Add Tag to add another line for more tags or ranges.
Add Tag to add another line for more tags or ranges.
QinQ Interface Configuration¶
Setting up QinQ interfaces is fairly simple:
Navigate to Interfaces > Assignments
Click the QinQ tab
Click
 Add to add a new QinQ entry
Add to add a new QinQ entryConfigure the QinQ entry as described in QinQ Interface Settings
Click Save to complete the interface
QinQ Example¶
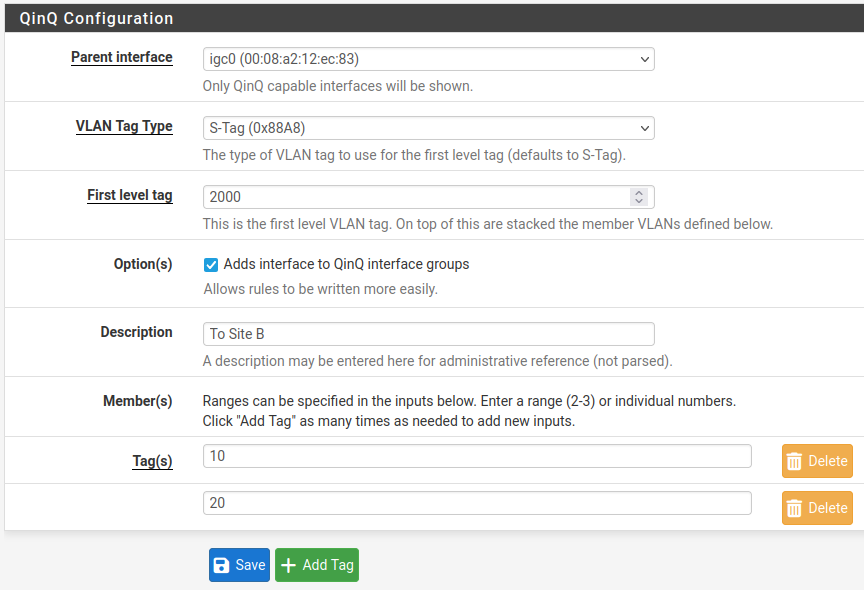
In the following example (Figure QinQ Basic Example), a QinQ
interface is configured to carry tagged traffic for VLANs 10 and 20
across the link on igc0 with a first level tag of 2000.
QinQ Basic Example¶
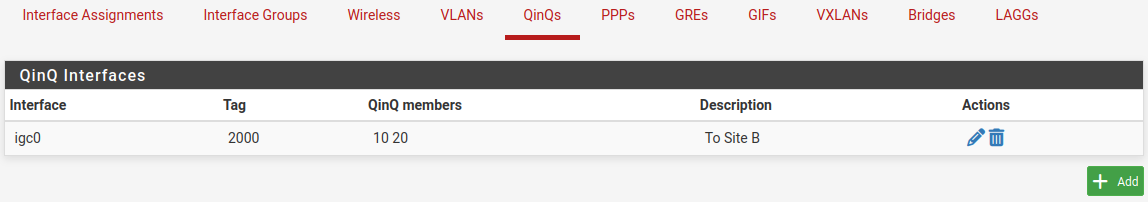
In Figure QinQ List, this entry is shown on the QinQ tab summary list.
QinQ List¶
The automatic interface group, shown in Figure QinQ Interface Group, must not be manually edited. Because these interfaces are not assigned, it is not possible to make alterations to the group without breaking it. To re-create the group, delete it from this list and then edit and save the QinQ instance again to add it back.
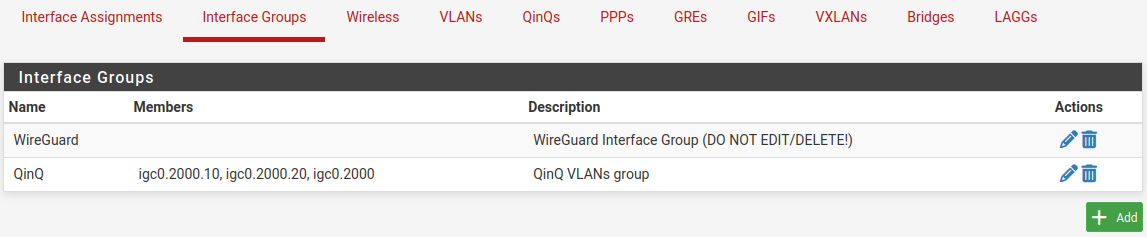
QinQ Interface Group¶
Rules may be added to the QinQ tab under Firewall > Rules to pass traffic in both directions across the QinQ links.
From here, how the QinQ interfaces are used is mostly up to the needs of the
network. Most likely, the resulting interfaces may be assigned and then
configured in some way, or bridged to their local equivalent VLANs (e.g. bridge
an assigned igc1.10 to igc0.2000.10 and so on).
The QinQ configuration will be roughly the same on both ends of the setup. For
example, if both sides use identical interface configurations, then traffic that
leaves Site A out on igc0.2000.10 will go through VLAN 2000 on igc0,
come out the other side on VLAN 2000 on igc0 at Site B, and then in
igc0.2000.10 at Site B.