Preparing a VPC¶
Using a Netgate appliance instance to protect VPC subnets requires the following:
One internet-facing subnet, to which the Netgate appliance instance will have its primary/WAN interface connected.
One or more private subnets, to which the Netgate appliance instance will have its secondary/LAN interface (and possibly additional optional interfaces) connected.
Separate routing tables for the internet-facing subnet and the private subnet(s).
If all of these are already in place with an existing VPC, feel free to skip ahead to Launching an Instance.
These instructions demonstrate how to create a single private subnet and set it up behind an instance of the Netgate® pfSense® Plus Firewall/VPN/Router appliance.
In the Amazon VPC Management Console, create a new VPC, subnets, and routing table(s).
Navigate to Your VPCs
Open the VPC Management Console
Click Your VPCs in the menu on the left side under the Virtual private cloud grouping
Click the Create VPC button
Configure the new VPC
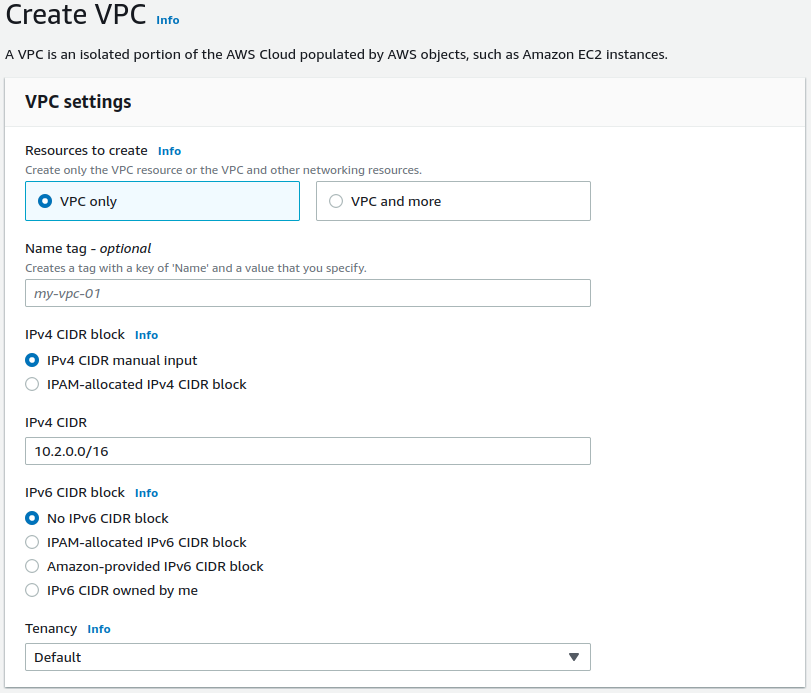
Optionally enter a Name tag
Enter the IPv4 CIDR network to use
If connecting to hosts in the VPC using a VPN from hosts at other sites in an organization’s infrastructure, be sure to select address space that does not conflict with the private address space used elsewhere by the organization.
Make sure the block is large enough to contain all subnets to include within it, optionally providing for future expansion. e.g. To use a
/24for an internet-facing subnet and a/24for a private network, the minimum CIDR block must be at least a/23to hold those two subnets. The maximum size block is a/16.For the purposes of this example, use
10.2.0.0/16.Leave the value of Tenancy set to Default
Click the Create VPC button
Create the public subnet(s)
Navigate to the Subnets view in the menu on the left side of the VPC Management Console
Click the Create Subnet button
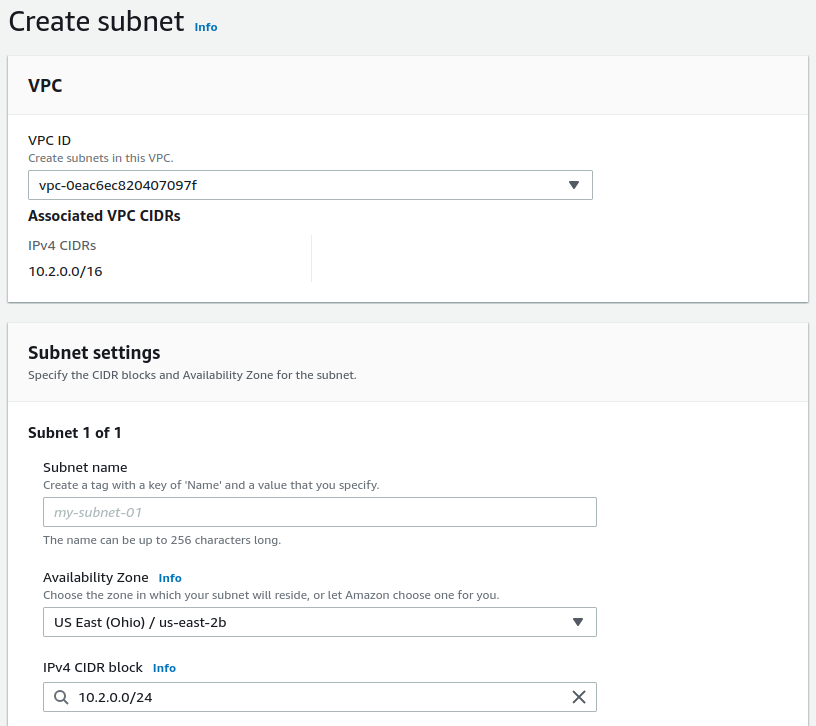
Select the newly created VPC from the VPC ID drop-down
Optionally enter a Subnet name
Optionally choose the desired Availability Zone
Enter the subnet to use for the internet-facing hosts in the IPv4 CIDR Block field
This subnet must be a block that is within the address space assigned to the VPC.
This is the subnet to which the WAN interface of the Netgate appliance instance is attached and could include any other hosts or appliances that should be available directly from the Internet and not protected behind the Netgate appliance.
For this example, use
10.2.0.0/24.Click the Create subnet button
Create the private subnet(s).
Navigate to the Subnets view in the menu on the left side of the VPC Management Console
The browser may still be in this view after completing the previous task.
Click the Create Subnet button again
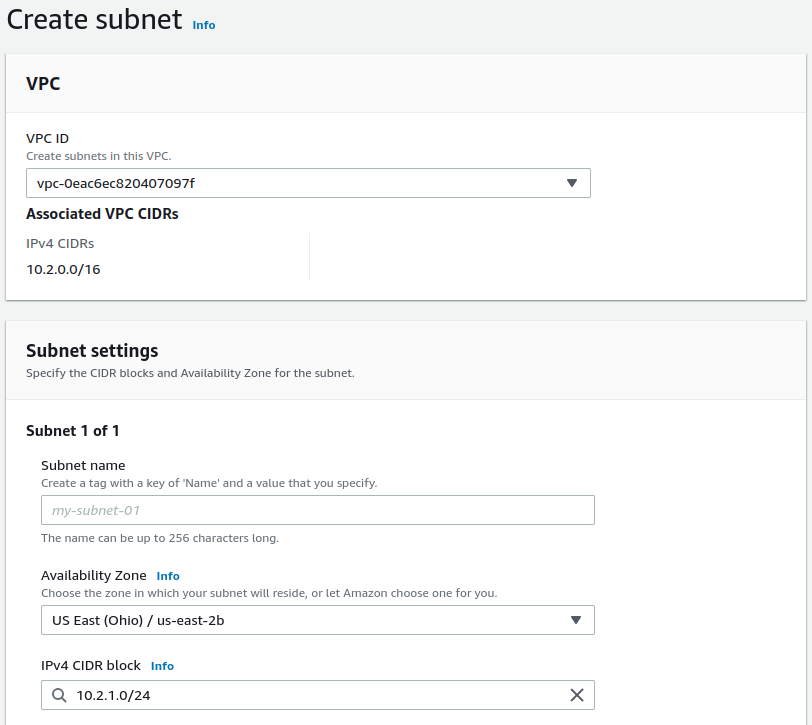
Select the same VPC from the VPC ID drop-down
Optionally enter a Subnet name
Optionally choose the same Availability Zone as the previous subnet
Enter the subnet to use for the private network in the IPv4 CIDR Block field
This subnet must be a block that is within the address space assigned to the VPC, and it must be distinct from the public subnet.
This is the subnet to which the LAN interface of the Netgate appliance instance is attached and could include any other hosts or appliances that should be protected behind the Netgate appliance.
For this example, use
10.2.1.0/24.Click the Create subnet button
Configure the route table
Both new subnets start out set to use a default route table automatically created for the VPC by AWS. The private subnet can continue to use that default table.
Create a new route table for the public subnet to override this behavior:
Navigate to the Route Tables view in the menu on the left side of the VPC Management Console
This view will contain all the existing route tables, and will at least contain the route table created by AWS for the VPN.
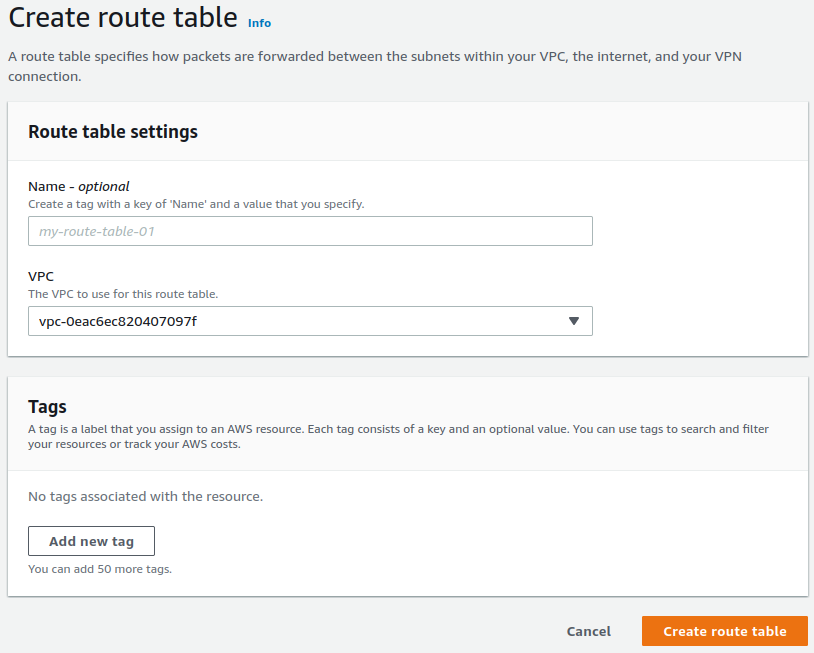
Click the Create route table button
Optionally enter a Name for the route table
Select the VPC
Click the Create route table button
Associate the public subnet with the newly created routing table
The public subnet is
10.2.0.0/24in this example.Navigate to the Subnets view on the left-hand side of the VPC Management Console.
Check the checkbox next to the public subnet
Scroll down to the information displayed for the selected subnet
The Details tab contains the CIDR block, VPC, and Availability Zone among other information.
Click the Route table tab
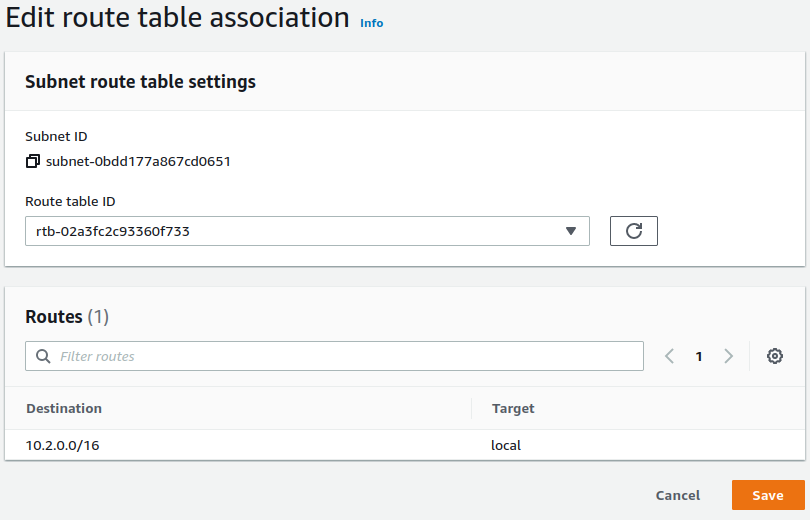
Click Edit route table association
Select the Route table ID corresponding to the route table created for the public subnet
Click the Save button
Create an Internet Gateway and attach it to the VPC
To send traffic from the public subnet to the Internet, the VPC requires a default route to an Internet Gateway. To create this gateway:
Navigate to the Internet gateways view in the menu on the left side of the VPC Management Console
Click the Create Internet Gateway button
Enter a Name tag for the gateway
Click the Create Internet Gateway button
The view should be filtered to display the new gateway. If it is not, then click the checkbox next to the newly created gateway entry in the list.
Click Actions
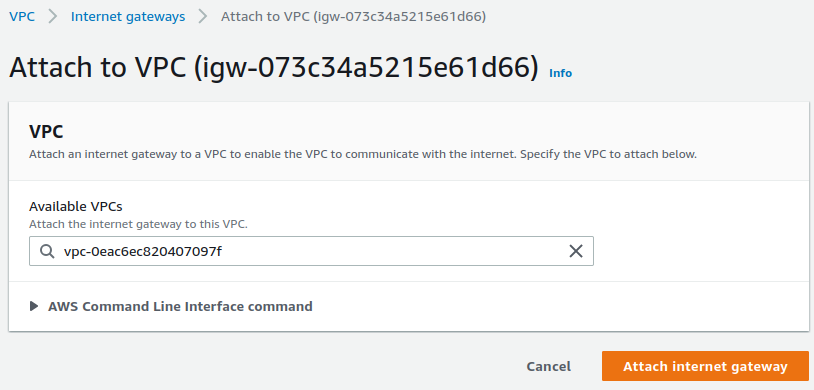
Click Attach to VPC
Select the VPC in the Available VPCs box
Click the Attach internet gateway button
Associate the gateway with the public route table
The route table for the public subnet must be updated so that it has a default route to the Internet Gateway.
Navigate to the Route Tables view on the left-hand side of the VPC Management Console.
Check the checkbox next to the route table for the public subnet
Scroll down to the details of the route table
Click the Routes tab
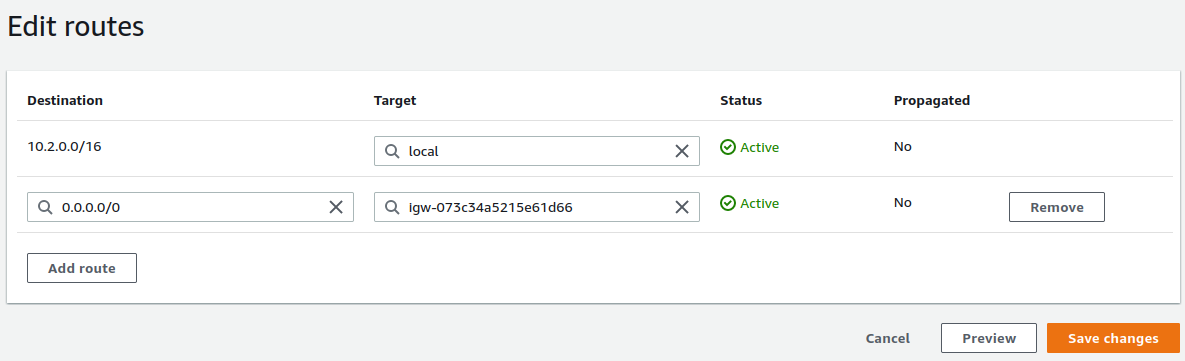
The Routes tab for this route table should contain a single route for the CIDR block of the VPC (
10.2.0.0/16in this example) that has a target of local.Click Edit routes
Click Add route
Click the Destination text box in the new row
Enter a Destination of
0.0.0.0/0Click the Target text box in the same row
Click Internet gateway from the list
Select the Internet Gateway created previously
The entry should be formatted similar to
igw-XXXXXXXXand will also have the name configured for the gateway.Click Save Changes
There are a few more VPC configuration changes that will be required later, but the next step is to launch a Netgate appliance instance.