Connecting to the RJ45 Console Port¶
There are times when directly accessing the console is required. Perhaps GUI or SSH access has been locked out, or the password has been lost or forgotten.
A separate adapter is required to make a connection between a computer and the firewall using the RJ45 serial port. This can be a direct RJ45-to-USB serial adapter or a standard USB-to-serial adapter and an RJ45-to-DB9 adapter or cable. It is also possible to utilize client hardware serial ports and compatible cables, but these ports are rare on modern hardware.
These are standard components, inexpensive and readily available from most retail outlets that sell computer cables.
Installing drivers and locating the port will vary depending on the third party device, consult its documentation for details.
Launch a Terminal Program¶
Use a terminal program to connect to the system console port. Some choices of terminal programs:
For Windows the best practice is to run PuTTY on Windows or SecureCRT. An example of how to configure PuTTY is below.
Warning
Do not use HyperTerminal.
For macOS the best practice is to run GNU screen, or cu. An
example of how to configure GNU screen is below.
For Linux the best practices are to run GNU screen, PuTTY on Linux,
minicom, or dterm. Examples of how to configure PuTTY and GNU
screen are below.
For FreeBSD the best practice is to run GNU screen or cu. An
example of how to configure GNU screen is below.
Client-Specific Examples¶
PuTTY on Windows¶
Open PuTTY and select Session under Category on the left-hand side.
Set the Connection type to Serial
Set Serial line to the console port determined previously
Set the Speed to
115200bits per second.Click the Open button
PuTTY will then display the console.
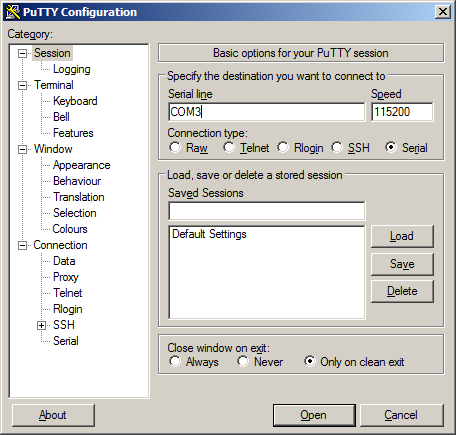
An example of using PuTTY on Windows¶
PuTTY on Linux¶
Open PuTTY from a terminal by typing
sudo puttyNote
The
sudocommand will prompt for the local workstation password of the current account.Set the Connection type to Serial
Set Serial line to
/dev/ttyUSB0Set the Speed to
115200bits per secondClick the Open button
PuTTY will then display the console.
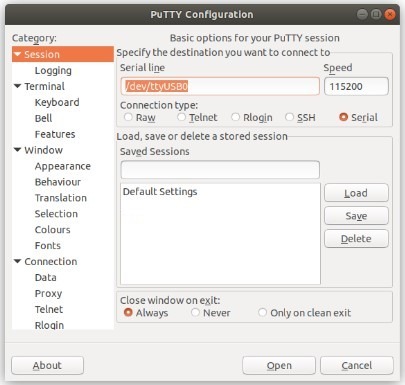
An example of using PuTTY on Linux¶
GNU screen¶
In many cases screen may be invoked simply by using the proper command line,
where <console-port> is the console port that was located above.
$ sudo screen <console-port> 115200
Note
The sudo command will prompt for the local workstation password of the
current account.
If portions of the text are unreadable but appear to be properly formatted, the
most likely culprit is a character encoding mismatch in the terminal. Adding the
-U parameter to the screen command line arguments forces it to use UTF-8
for character encoding:
$ sudo screen -U <console-port> 115200
Terminal Settings¶
The settings to use within the terminal program are:
- Speed:
115200baud, the speed of the BIOS- Data bits:
8- Parity:
None
- Stop bits:
1- Flow Control:
Off or XON/OFF.
Warning
Hardware flow control (RTS/CTS) must be disabled.
Terminal Optimization¶
Beyond the required settings there are additional options in terminal programs which will help input behavior and output rendering to ensure the best experience. These settings vary location and client, and may not be available in all clients or terminals.
These are:
- Terminal Type:
xtermThis setting may be under Terminal, Terminal Emulation, or similar areas.
- Color Support:
ANSI colors / 256 Color / ANSI with 256 Colors
This setting may be under Terminal Emulation, Window Colors, Text, Advanced Terminfo, or similar areas.
- Character Set / Character Encoding:
UTF-8This setting may be under Terminal Appearance, Window Translation, Advanced International, or similar areas. In GNU screen this is activated by passing the
-Uparameter.- Line Drawing:
Look for and enable setting such as “Draw lines graphically”, “Use Unicode graphics characters”, and/or “Use Unicode line drawing code points”.
These settings may be under Terminal Appearance, Window Translation, or similar areas.
- Function Keys / Keypad:
Xterm R6In Putty this is under Terminal > Keyboard and is labeled The Function Keys and Keypad.
- Font:
For the best experience, use a modern monospaced Unicode font such as DejaVu Sans Mono, Liberation Mono, Monaco, Consolas, Fira Code, or similar.
This setting may be under Terminal Appearance, Window Appearance, Text, or similar areas.
What’s Next?¶
After connecting a terminal client, it may not immediately see any output. This could be because the device has already finished booting, or it may be that the device is waiting for some other input.
If the device does not yet have power applied, plug it in and monitor the terminal output.
If the device is already powered on, try pressing Space. If there is still
no output, press Enter. If the device was booted, it may re-display the
console menu or login prompt, or produce other output indicating its status.
From the console, a variety of things are possible, such as changing interface addresses. There is a full explanation of every console menu option in the pfSense software documentation.
Troubleshooting¶
Serial Device Missing¶
With a USB serial console there are a few reasons why the serial port may not be present in the client operating system, including:
- No Power
Some models require power before the client can connect to the USB serial console.
- USB Cable Not Plugged In
For USB consoles, the USB cable may not be fully engaged on both ends. Gently, but firmly, ensure the cable has a good connection on both sides.
- Bad USB Cable
Some USB cables are not suitable for use as data cables. For example, some cables are only capable of delivering power for charging devices and not acting as data cables. Others may be of low quality or have poor or worn connectors.
The ideal cable to use is the one that came with the device. Failing that, ensure the cable is of the correct type and specifications, and try multiple cables.
- Wrong Device
In some cases there may be multiple serial devices available. Ensure the one used by the serial client is the correct one. Some devices expose multiple ports, so using the incorrect port may lead to no output or unexpected output.
- Hardware Failure
There could be a hardware failure preventing the serial console from working. Contact Netgate TAC for assistance.
No Serial Output¶
If there is no output at all, check the following items:
- USB Cable Not Plugged In
For USB consoles, the USB cable may not be fully engaged on both ends. Gently, but firmly, ensure the cable has a good connection on both sides.
- Wrong Device
In some cases there may be multiple serial devices available. Ensure the one used by the serial client is the correct one. Some devices expose multiple ports, so using the incorrect port may lead to no output or unexpected output.
- Wrong Terminal Settings
Ensure the terminal program is configured for the correct speed. The default BIOS speed is
115200, and many other modern operating systems use that speed as well.Some older operating systems or custom configurations may use slower speeds such as
9600or38400.- Device OS Serial Console Settings
Ensure the operating system is configured for the proper console (e.g.
ttyS1in Linux). Consult the various operating installation guides on this site for further information.
PuTTY has issues with line drawing¶
PuTTY generally handles most cases OK but can have issues with line drawing characters on certain platforms.
These settings seem to work best (tested on Windows):
- Window:
- Columns x Rows:
80x24
- Window > Appearance:
- Font:
Courier New 10pt or Consolas 10pt
- Window > Translation:
- Remote Character Set:
Use font encoding or UTF-8
- Handling of line drawing characters:
Use font in both ANSI and OEM modes or Use Unicode line drawing code points
- Window > Colours:
- Indicate bolded text by changing:
The colour
Garbled Serial Output¶
If the serial output appears to be garbled, missing characters, binary, or random characters check the following items:
- Flow Control
In some cases flow control can interfere with serial communication, causing dropped characters or other issues. Disabling flow control in the client can potentially correct this problem.
On PuTTY and other GUI clients there is typically a per-session option to disable flow control. In PuTTY, the Flow Control option is in the settings tree under Connection, then Serial.
To disable flow control in GNU Screen, add the
-ixonand/or-ixoffparameters after the serial speed as in the following example:$ sudo screen <console port> 115200,-ixon
- Terminal Speed
Ensure the terminal program is configured for the correct speed. (See No Serial Output)
- Character Encoding
Ensure the terminal program is configured for the proper character encoding, such as UTF-8 or Latin-1, depending on the operating system. (See GNU Screen)
Serial Output Stops After the BIOS¶
If serial output is shown for the BIOS but stops afterward, check the following items:
- Terminal Speed
Ensure the terminal program is configured for the correct speed for the installed operating system. (See No Serial Output)
- Device OS Serial Console Settings
Ensure the installed operating system is configured to activate the serial console and that it is configured for the proper console (e.g.
ttyS1in Linux). Consult the various operating installation guides on this site for further information.- Bootable Media
If booting from a USB flash drive, ensure that the drive was written correctly and contains a bootable operating system image.