Tip
This is the documentation for the v21.03 version. Looking for the documentation of the latest version? Have a look here.
Edge Router Speaking eBGP with Static Redistribution for IPv4 And IPv6¶
Use Case¶
Especially in cases where an enterprise is multi-homed with its own block of network addresses, it may become necessary to configure dynamic routing between network service providers. This is accomplished by use of external BGP (eBGP).
In this use case, the enterprise will use TNSR to speak eBGP with two network service providers in order to exchange routes which may be redistributed from static/connected routing.
Example Scenario¶
In this example, the enterprise using TNSR will have a fictitious autonomous system number (ASN) of 65505. The network service providers in this example will have ASNs of 65510 and 65520. The enterprise using TNSR will redistribute a single /24 network from static into BGP. That network will then be advertised to each of the service providers. The service providers will announce a full routing table to the TNSR instance.
Scenario Topology¶
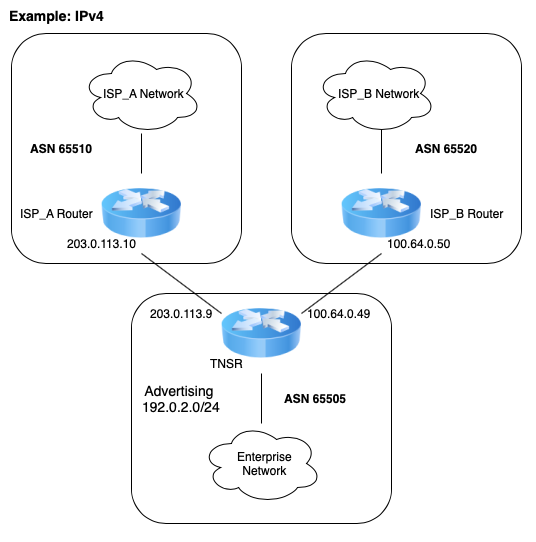
TNSR BGP Router (IPv4)¶
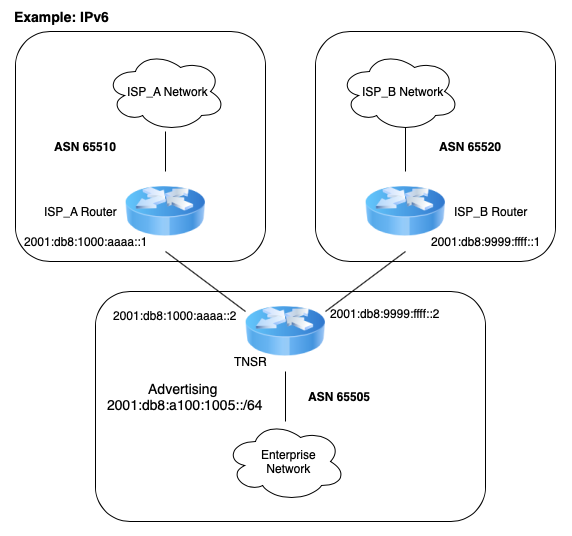
TNSR BGP Router (IPv6)¶
Item |
Value |
|---|---|
VRF Name |
default |
TNSR Autonomous System Number |
65505 |
ISP_A Autonomous System Number |
65510 |
ISP_B Autonomous System Number |
65520 |
IPv4 Network to be announced |
192.0.2.0/24 |
IPv6 Network to be announced |
2001:db8:a100:1005::/64 |
TNSR to ISP_A IPv4 Network Address |
203.0.113.8/30 |
TNSR to ISP_A IPv6 Global Address |
2001:db8:fa00:ffaa::/64 |
TNSR to ISP_B IPv4 Network Address |
100.64.0.48/30 |
TNSR to ISP_B IPv6 Global Address |
2001:db8:fb00:ffbb::/64 |
TNSR Configuration Steps¶
Step 1: Configure Interfaces¶
tnsr# conf
tnsr(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/13/0
tnsr(config-interface)# description "To ISP A"
tnsr(config-interface)# ip address 203.0.113.9/30
tnsr(config-interface)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:1000:aaaa::2/64
tnsr(config-interface)# enable
tnsr(config-interface)# exit
tnsr(config)#
tnsr(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/14/0
tnsr(config-interface)# description "To ISP B"
tnsr(config-interface)# ip address 100.64.0.49/30
tnsr(config-interface)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:9999:ffff::2/64
tnsr(config-interface)# enable
tnsr(config-interface)# exit
tnsr(config)#
Step 2: Enable BGP¶
tnsr(config)# route dynamic bgp
tnsr(config-frr-bgp)# enable
tnsr(config-frr-bgp)# exit
tnsr(config)#
Step 3: Create prefix-lists for route export via BGP¶
tnsr(config)# route dynamic prefix-list EXPORT_IPv4
tnsr(config-prefix-list)# description "IPv4 Routes to Export"
tnsr(config-prefix-list)# seq 10 permit 192.0.2.0/24
tnsr(config-prefix-list)# exit
tnsr(config)#
tnsr(config)# route dynamic prefix-list EXPORT_IPv6
tnsr(config-prefix-list)# description "IPv6 Routes to Export"
tnsr(config-prefix-list)# seq 10 permit 2001:db8:a100:1005::/64
tnsr(config-prefix-list)# exit
tnsr(config)#
Step 4: Create static route for networks to be advertised in BGP¶
tnsr(config)# route table ipv4-VRF:0
tnsr(config-route-table)# route 192.0.2.0/24
tnsr(config-rttbl4-next-hop)# next-hop 1 via local
tnsr(config-rttbl4-next-hop)# exit
tnsr(config-route-table)# exit
tnsr(config)# route table ipv6-VRF:0
tnsr(config-route-table)# route 2001:db8:a100:1005::/64
tnsr(config-rttbl6-next-hop)# next-hop 1 via local
tnsr(config-rttbl6-next-hop)# exit
tnsr(config-route-table)# exit
tnsr(config)#
Step 5: Configure BGP global options¶
tnsr(config)# route dynamic bgp
tnsr(config-frr-bgp)# server vrf default
tnsr(config-bgp)# as-number 65505
tnsr(config-bgp)# router-id 203.0.113.9
tnsr(config-bgp)# address-family ipv4 unicast
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# redistribute kernel
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# exit
tnsr(config-bgp)# address-family ipv6 unicast
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# redistribute kernel
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# exit
tnsr(config-bgp)#
Step 6: Configure BGP global neighbor options¶
tnsr(config-bgp)# neighbor 203.0.113.10
tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 65510
tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# description "ISP_A IPv4"
tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# enable
tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# exit
tnsr(config-bgp)# neighbor 2001:db8:1000:aaaa::1
tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 65510
tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# description "ISP_A IPv6"
tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# enable
tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# exit
tnsr(config-bgp)# neighbor 100.64.0.50
tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 65520
tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# description "ISP_B IPv4"
tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# enable
tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# exit
tnsr(config-bgp)# neighbor 2001:db8:9999:ffff::1
tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 65520
tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# description "ISP_B IPv6"
tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# enable
tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# exit
tnsr(config-bgp)#
Step 7: Configure BGP neighbor address-family IPv4 unicast options¶
tnsr(config-bgp)# address-family ipv4 unicast
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# neighbor 203.0.113.10
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# prefix-list EXPORT_IPv4 out
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# activate
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# exit
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# neighbor 100.64.0.50
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# prefix-list EXPORT_IPv4 out
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# activate
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# exit
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# exit
tnsr(config-bgp)#
Step 8: Configure BGP neighbor address-family IPv6 unicast options¶
tnsr(config-bgp)# address-family ipv6 unicast
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# neighbor 2001:db8:1000:aaaa::1
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# prefix-list EXPORT_IPv6 out
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# activate
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# exit
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# neighbor 2001:db8:9999:ffff::1
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# prefix-list EXPORT_IPv6 out
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# activate
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# exit
tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# exit
tnsr(config-bgp)# exit
tnsr(config-frr-bgp)# exit
tnsr(config)#