ACL and NAT Interaction¶
When NAT is active, ACL rules are always processed before NAT on interfaces where NAT is applied, in any direction.
The remainder of the section refers to the following example static NAT rule:
nat static mapping tcp local 10.2.0.129 22 external 203.0.113.2 222
In this example, the rule is applied on the external-facing interface
containing 203.0.113.2.
Inbound ACL Rules¶
ACL Rules set to be processed in the inbound direction on an interface
(access-list input acl <name> sequence <seq>) will match on the external
address and/or port in a static NAT rule. In the above example, this means
an inbound ACL would match on a destination IP address of 203.0.113.2 and/or
a destination port of 222.
Outbound ACL Rules¶
ACL Rules set to be processed in the outbound direction on an interface
(access-list output acl <name> sequence <seq>) will match on the local
address and/or port in a static NAT rule. In the above example, this means
an outbound ACL would match on a source IP address of 10.2.0.129 and/or a
source port of 22.
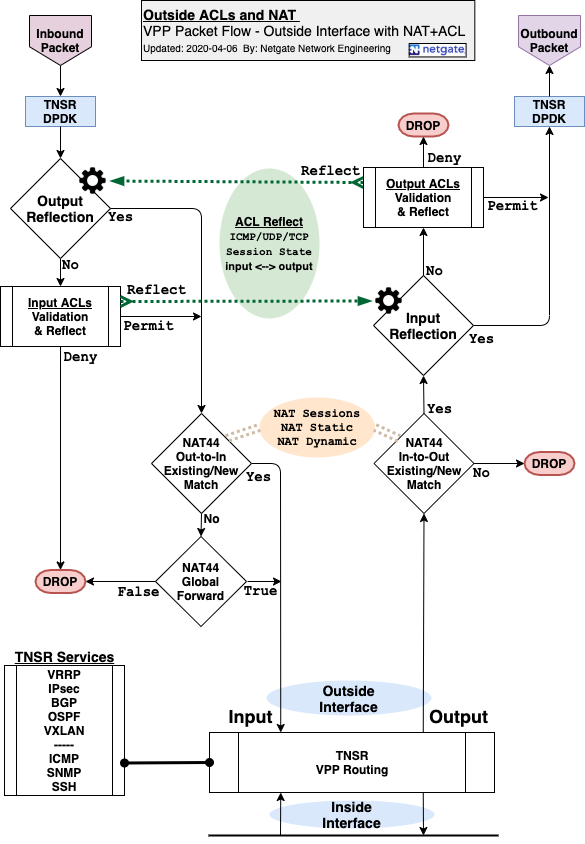
ACL and NAT Flow Chart¶
This diagram shows the logic behind how TNSR processes packets with ACLs and
outside NAT active on an interface. The flow depends on a number of factors such
as whether ACLs use the reflect action and whether NAT forwarding is active.