Tip
This is the documentation for the 22.10 version. Looking for the documentation of the latest version? Have a look here.
Service Provider Route Reflectors and Client for iBGP IPv4¶
Use Case¶
In large service provider networks it is necessary to divide the routing functionality into two or more layers: a backbone layer and a gateway layer. This allows backbone routers to be focused on core routing and switching to/from other areas of the routing domain, and gateway routers may then be focused on interconnecting other service provider customers.
Example Scenario¶
In this example, the service provider will have a fictitious autonomous system
number (ASN) of 65505, Each network POP, of which only one will be detailed
here, will feature 2 backbone routers which will be configured as
route-reflectors. These backbone routers will be participating in BGP Cluster
ID 100. Other POPs will likely be different Cluster IDs.
There will also be a single gateway router which will be a client of the backbone route-reflectors. Of course, in real world scenarios there would likely be many more gateway routers, each serving a full complement of customers.
Item |
Value |
|---|---|
VRF Name |
default |
TNSR Autonomous System Number |
65505 |
IPv4 Networks to be announced |
192.0.2.0/24, 203.0.113.0/24 |
BGP Route-Reflector Cluster ID |
100 |
Scenario Topology¶
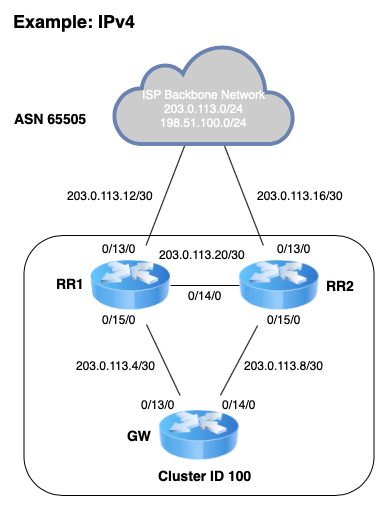
TNSR BGP Route Reflector¶
TNSR Configuration Steps¶
Step 1: Configure Interfaces¶
RR1:
rr1 tnsr# conf
rr1 tnsr(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/13/0
rr1 tnsr(config-interface)# description "To Backbone Network"
rr1 tnsr(config-interface)# ip address 203.0.113.13/30
rr1 tnsr(config-interface)# enable
rr1 tnsr(config-interface)# exit
rr1 tnsr(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/14/0
rr1 tnsr(config-interface)# description "To RR2 Router"
rr1 tnsr(config-interface)# ip address 203.0.113.21/30
rr1 tnsr(config-interface)# enable
rr1 tnsr(config-interface)# exit
rr1 tnsr(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/15/0
rr1 tnsr(config-interface)# description "To GW router"
rr1 tnsr(config-interface)# ip address 203.0.113.5/30
rr1 tnsr(config-interface)# enable
rr1 tnsr(config-interface)# exit
rr1 tnsr(config)#
RR2:
rr2 tnsr# conf
rr2 tnsr(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/13/0
rr2 tnsr(config-interface)# description "To Backbone Network"
rr2 tnsr(config-interface)# ip address 203.0.113.17/30
rr2 tnsr(config-interface)# enable
rr2 tnsr(config-interface)# exit
rr2 tnsr(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/14/0
rr2 tnsr(config-interface)# description "To RR1 Router"
rr2 tnsr(config-interface)# ip address 203.0.113.22/30
rr2 tnsr(config-interface)# enable
rr2 tnsr(config-interface)# exit
rr2 tnsr(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/15/0
rr2 tnsr(config-interface)# description "To GW router"
rr2 tnsr(config-interface)# ip address 203.0.113.9/30
rr2 tnsr(config-interface)# enable
rr2 tnsr(config-interface)# exit
rr2 tnsr(config)#
GW:
gw tnsr# conf
gw tnsr(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/13/0
gw tnsr(config-interface)# description "To RR1 Router"
gw tnsr(config-interface)# ip address 203.0.113.6/30
gw tnsr(config-interface)# enable
gw tnsr(config-interface)# exit
gw tnsr(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/14/0
gw tnsr(config-interface)# description "To RR2 Router"
gw tnsr(config-interface)# ip address 203.0.113.10/30
gw tnsr(config-interface)# enable
gw tnsr(config-interface)# exit
gw tnsr(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/15/0
gw tnsr(config-interface)# desc "To Customer Router"
gw tnsr(config-interface)# ip address 203.0.113.25/30
gw tnsr(config-interface)# enable
gw tnsr(config-interface)# exit
gw tnsr(config)#
Step 2: Enable BGP¶
RR1:
rr1 tnsr(config)# route dynamic bgp
rr1 tnsr(config-frr-bgp)# enable
rr1 tnsr(config-frr-bgp)# exit
rr1 tnsr(config)#
RR2:
rr2 tnsr(config)# route dynamic bgp
rr2 tnsr(config-frr-bgp)# enable
rr2 tnsr(config-frr-bgp)# exit
rr2 tnsr(config)#
GW:
gw tnsr(config)# route dynamic bgp
gw tnsr(config-frr-bgp)# enable
gw tnsr(config-frr-bgp)# exit
gw tnsr(config)#
Step 3: Create prefix-lists for route import into BGP on Route-Reflectors¶
RR1:
rr1 tnsr(config)# route dynamic prefix-list REDISTRIBUTE_IPv4
rr1 tnsr(config-prefix-list)# description "IPv4 Routes to Import"
rr1 tnsr(config-prefix-list)# seq 10 permit 192.0.2.0/24
rr1 tnsr(config-prefix-list)# seq 20 permit 203.0.113.0/24
rr1 tnsr(config-prefix-list)# exit
rr1 tnsr(config)#
RR2:
rr2 tnsr(config)# route dynamic prefix-list REDISTRIBUTE_IPv4
rr2 tnsr(config-prefix-list)# description "IPv4 Routes to Import"
rr2 tnsr(config-prefix-list)# seq 10 permit 192.0.2.0/24
rr2 tnsr(config-prefix-list)# seq 20 permit 203.0.113.0/24
rr2 tnsr(config-prefix-list)# exit
rr2 tnsr(config)#
Step 4: Create route-map for route import into iBGP on route-reflectors¶
RR1:
rr1 tnsr(config)# route dynamic route-map REDISTRIBUTE_IPv4
rr1 tnsr(config-route-map)# sequence 10
rr1 tnsr(config-route-map-rule)# policy permit
rr1 tnsr(config-route-map-rule)# match ip address prefix-list REDISTRIBUTE_IPv4
rr1 tnsr(config-route-map-rule)# set origin igp
rr1 tnsr(config-route-map-rule)# exit
rr1 tnsr(config-route-map)# exit
rr1 tnsr(config)#
RR2:
rr2 tnsr(config)# route dynamic route-map REDISTRIBUTE_IPv4
rr2 tnsr(config-route-map)# sequence 10
rr2 tnsr(config-route-map-rule)# policy permit
rr2 tnsr(config-route-map-rule)# match ip address prefix-list REDISTRIBUTE_IPv4
rr2 tnsr(config-route-map-rule)# set origin igp
rr2 tnsr(config-route-map-rule)# exit
rr2 tnsr(config-route-map)# exit
rr2 tnsr(config)#
Step 5: Create static route for networks to be advertised in BGP¶
RR1:
rr1 tnsr(config)# route table ipv4-VRF:0
rr1 tnsr(config-route-table)# route 192.0.2.0/24
rr1 tnsr(config-rttbl4-next-hop)# next-hop 1 via local
rr1 tnsr(config-rttbl4-next-hop)# exit
rr1 tnsr(config-route-table)# route 203.0.113.0/24
rr1 tnsr(config-rttbl4-next-hop)# next-hop 1 via local
rr1 tnsr(config-rttbl4-next-hop)# exit
rr1 tnsr(config-route-table)# exit
rr1 tnsr(config)#
RR2:
rr2 tnsr(config)# route table ipv4-VRF:0
rr2 tnsr(config-route-table)# route 192.0.2.0/24
rr2 tnsr(config-rttbl4-next-hop)# next-hop 1 via local
rr2 tnsr(config-rttbl4-next-hop)# exit
rr2 tnsr(config-route-table)# route 203.0.113.0/24
rr2 tnsr(config-rttbl4-next-hop)# next-hop 1 via local
rr2 tnsr(config-rttbl4-next-hop)# exit
rr2 tnsr(config-route-table)# exit
rr2 tnsr(config)#
Step 6: Configure BGP global options¶
RR1:
rr1 tnsr(config)# route dynamic bgp
rr1 tnsr(config-frr-bgp)# server vrf default
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp)# as-number 65505
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp)# router-id 203.0.113.21
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp)# cluster-id 0.0.0.100
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp)# no ebgp-requires-policy
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp)# no network import-check
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp)# address-family ipv4 unicast
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# redistribute kernel route-map REDISTRIBUTE_IPv4
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# exit
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp)#
RR2:
rr2 tnsr(config)# route dynamic bgp
rr2 tnsr(config-frr-bgp)# server vrf default
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp)# as-number 65505
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp)# router-id 203.0.113.22
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp)# cluster-id 0.0.0.100
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp)# no ebgp-requires-policy
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp)# no network import-check
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp)# address-family ipv4 unicast
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# redistribute kernel route-map REDISTRIBUTE_IPv4
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# exit
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp)#
GW:
gw tnsr(config)# route dynamic bgp
gw tnsr(config-frr-bgp)# server vrf default
gw tnsr(config-bgp)# as-number 65505
gw tnsr(config-bgp)# router-id 203.0.113.6
gw tnsr(config-bgp)# no ebgp-requires-policy
gw tnsr(config-bgp)# no network import-check
gw tnsr(config-bgp)#
Step 7: Configure iBGP peer-group for backbone route-reflectors and add neighbor¶
RR1:
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp)# neighbor iBGP
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 65505
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# description "iBGP Sessions"
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# update-source GigabitEthernet0/14/0
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# enable
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# exit
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp)# neighbor 203.0.113.22
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# peer-group iBGP
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# enable
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# exit
RR2:
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp)# neighbor iBGP
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 65505
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# description "iBGP Sessions"
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# update-source GigabitEthernet0/14/0
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# enable
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# exit
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp)# neighbor 203.0.113.21
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# peer-group iBGP
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# enable
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# exit
Step 8: Configure RR-CLIENT peer-group for route-reflector clients and add neighbor¶
RR1:
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp)# neighbor RR-CLIENT
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 65505
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# description "RR-Client Sessions"
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# update-source GigabitEthernet0/15/0
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# enable
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# exit
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp)# neighbor 203.0.113.6
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# peer-group RR-CLIENT
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# enable
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# exit
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp)#
RR2:
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp)# neighbor RR-CLIENT
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 65505
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# description "RR-Client Sessions"
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# update-source GigabitEthernet0/15/0
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# enable
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# exit
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp)# neighbor 203.0.113.10
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# peer-group RR-CLIENT
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# enable
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# exit
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp)#
Step 9: Configure both peer-group address-family options on route-reflectors¶
RR1:
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp)# address-family ipv4 unicast
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# neighbor iBGP
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# next-hop-self
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# activate
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# exit
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# neighbor RR-CLIENT
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# route-reflector-client
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# activate
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# exit
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# exit
rr1 tnsr(config-bgp)#
RR2:
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp)# address-family ipv4 unicast
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# neighbor iBGP
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# next-hop-self
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# activate
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# exit
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# neighbor RR-CLIENT
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# route-reflector-client
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# activate
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# exit
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# exit
rr2 tnsr(config-bgp)#
Step 10: Configure iBGP on gateway router to both route-reflectors¶
GW:
gw tnsr(config-bgp)# neighbor 203.0.113.5
gw tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 65505
gw tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# description "RR1 Session"
gw tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# update-source GigabitEthernet0/13/0
gw tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# enable
gw tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# exit
gw tnsr(config-bgp)# neighbor 203.0.113.9
gw tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 65505
gw tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# description "RR2 Session"
gw tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# update-source GigabitEthernet0/14/0
gw tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# enable
gw tnsr(config-bgp-neighbor)# exit
gw tnsr(config-bgp)# address-family ipv4 unicast
gw tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# neighbor 203.0.113.5
gw tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# activate
gw tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# exit
gw tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# neighbor 203.0.113.9
gw tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# activate
gw tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni-nbr)# exit
gw tnsr(config-bgp-ip4uni)# exit
gw tnsr(config-bgp)#